The Ultimate Guide To Brick Height: Essential Measurements And Applications
What is "brick height"? The height of a brick is a crucial aspect that determines the structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and functionality of brickwork.
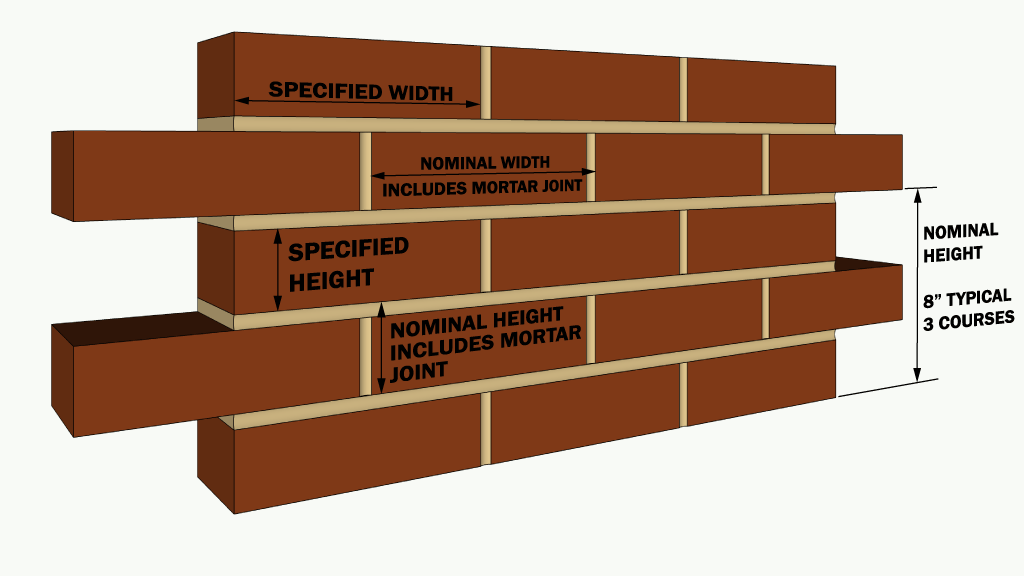
Brick height is typically measured in courses, which refer to horizontal layers of bricks. Each course consists of bricks stacked on top of each other, with mortar joints in between. The height of a single brick, along with the thickness of the mortar joints, determines the overall height of a course.
The importance of brick height cannot be overstated. It influences the strength and stability of brick structures. Bricks with appropriate height provide better load-bearing capacity, ensuring the longevity and safety of buildings. Moreover, brick height plays a significant role in the aesthetic appearance of brickwork. Different brick heights can create diverse patterns, textures, and visual effects, enhancing the architectural appeal of structures.
Throughout history, brick height has evolved based on construction techniques, regional preferences, and the availability of materials. In ancient times, bricks were often taller and narrower, while modern bricks tend to be shorter and wider. These variations in brick height reflect the changing needs and advancements in construction practices.
Brick Height
Brick height is a crucial aspect of brickwork, influencing its structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and functionality. Here are six key aspects to consider:
- Strength and Stability: Brick height affects the load-bearing capacity and durability of brick structures.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Different brick heights create diverse patterns and textures, enhancing the visual impact of brickwork.
- Construction Techniques: Brick height is influenced by construction methods and regional preferences.
- Historical Evolution: Brick height has evolved over time, reflecting advancements in construction practices.
- Material Availability: The availability of materials, such as clay and firing techniques, can impact brick height.
- Functional Considerations: Brick height can affect factors like thermal insulation and moisture resistance.
These key aspects are interconnected and play a vital role in determining the overall quality and performance of brickwork. For instance, taller bricks may provide better structural strength, while shorter bricks might be more suitable for creating intricate patterns. The choice of brick height should be carefully considered based on the specific requirements of the project, taking into account factors such as load-bearing needs, aesthetic preferences, and construction feasibility.
Strength and Stability
Brick height plays a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of brick structures. Taller bricks, with a larger surface area, provide better load-bearing capacity compared to shorter bricks. This is because taller bricks distribute the weight more evenly, reducing stress concentrations and increasing the overall stability of the structure.
- Load-bearing Walls: In load-bearing walls, which support the weight of the building above, taller bricks are preferred. They can withstand higher compressive forces and prevent the walls from buckling or collapsing.
- Arches and Vaults: Taller bricks are also advantageous in constructing arches and vaults, which are curved structures that transfer weight and create open spaces. The larger surface area of taller bricks provides a more secure base for the arch or vault, preventing it from sagging or collapsing under load.
- Durability: Taller bricks, with their increased mass and density, offer better resistance to weathering and erosion. They are less prone to cracking or chipping, which can compromise the structural integrity of the building over time.
In conclusion, the strength and stability of brick structures are directly influenced by the height of the bricks used. Taller bricks provide superior load-bearing capacity, enhanced durability, and greater stability, making them ideal for load-bearing walls, arches, vaults, and other structures that require high structural performance.
Aesthetic Appeal
Brick height plays a pivotal role in enhancing the aesthetic appeal of brickwork, offering architects and designers a versatile medium for creating visually striking and distinctive structures. The variation in brick heights allows for the creation of diverse patterns, textures, and visual effects, transforming brickwork from a mere structural element into an integral part of the building's architectural expression.
The use of bricks with varying heights enables the creation of intricate patterns and textures that can add depth, character, and visual interest to facades, walls, and other architectural features. For instance, alternating courses of bricks with different heights can create a striking striped effect, while bricks laid in a herringbone pattern add a touch of sophistication and elegance. Moreover, bricks of varying heights can be used to create decorative details such as arches, cornices, and quoins, further enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the structure.
The significance of aesthetic appeal in brickwork cannot be overstated. A well-designed brick facade can significantly enhance the curb appeal of a building, making it more visually appealing and attractive. This, in turn, can have a positive impact on the building's value, desirability, and overall perception. Moreover, the aesthetic appeal of brickwork can contribute to the character and identity of a neighborhood or city, creating a visually cohesive and pleasing built environment.
In conclusion, the connection between brick height and aesthetic appeal is undeniable. Different brick heights provide architects and designers with a powerful tool to create visually stunning and distinctive brickwork that enhances the overall architectural expression of a building. Understanding this connection is essential for architects, designers, and builders alike, as it allows them to harness the full potential of brickwork as both a structural and aesthetic element.
Construction Techniques
The connection between construction techniques, regional preferences, and brick height is significant in understanding the evolution and diversity of brickwork around the world. Construction techniques and regional preferences have a direct impact on the choice of brick height, influencing the structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and functionality of brick structures.
Construction methods, such as the type of bonding pattern used, can influence brick height. For instance, in stretcher bond, where bricks are laid in parallel rows, taller bricks may be preferred to create a stronger and more stable wall. In header bond, where the headers (short ends) of the bricks face outward, shorter bricks might be more suitable to achieve the desired aesthetic effect.
Regional preferences also play a role in determining brick height. In areas with abundant clay and traditional brick-making techniques, taller bricks may be more common. In contrast, regions with limited clay resources or different construction practices may favor shorter bricks.
Understanding the connection between construction techniques, regional preferences, and brick height is crucial for architects, builders, and historians. It allows them to appreciate the cultural and historical context of brickwork, make informed decisions about brick selection and construction methods, and preserve the authenticity of historic structures.
Historical Evolution
The historical evolution of brick height is deeply intertwined with the development of construction practices and technologies. As construction methods evolved over time, so too did the dimensions and characteristics of bricks.
In ancient times, bricks were often taller and narrower, due to the limitations of hand-molding techniques and the need for structural stability in load-bearing walls. As construction techniques advanced and new materials were introduced, bricks became shorter and wider, allowing for more efficient construction and a wider range of architectural possibilities.
For instance, the development of the firing process, which hardens and strengthens clay bricks, enabled the production of shorter and wider bricks without compromising their structural integrity. This advancement led to the widespread use of shorter bricks in the construction of buildings and structures, such as the iconic Roman aqueducts and the Great Wall of China.
Understanding the historical evolution of brick height is crucial for architects, builders, and historians alike. It provides insights into the cultural and technological context of brickwork, allowing for informed decision-making in the design and restoration of historic structures. Moreover, it helps us appreciate the ingenuity and adaptability of builders throughout history, who continuously refined and improved construction techniques to meet the demands of their time.
Material Availability
The availability of materials, particularly clay, and the advancements in firing techniques have a significant impact on brick height. Clay is the primary raw material used in brick production, and its properties, such as composition, texture, and firing temperature, can influence the size and shape of the finished bricks.
In regions with abundant clay resources, taller bricks may be more common, as there is less need to conserve materials. For example, in ancient Mesopotamia, where clay was plentiful, builders used tall, thin bricks to construct monumental structures such as the ziggurats.
Firing techniques also play a crucial role in determining brick height. Bricks fired at higher temperatures tend to be harder and more durable, allowing them to be made thinner and wider while maintaining their structural integrity. This advancement enabled the production of shorter and wider bricks, which became popular in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance periods.
Understanding the connection between material availability and brick height is essential for architects, builders, and historians. It helps them appreciate the cultural and technological context of brickwork, make informed decisions about brick selection and construction methods, and preserve the authenticity of historic structures.
Functional Considerations
The choice of brick height can have significant implications for the thermal insulation and moisture resistance of a building. These functional considerations should be carefully evaluated during the design and construction process to ensure the building meets the desired performance criteria.
- Thermal Insulation: Taller bricks, with their increased mass, provide better thermal insulation compared to shorter bricks. The greater mass helps to absorb and store heat, reducing the rate of heat transfer through the wall. This can lead to reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling, resulting in lower operating costs and improved occupant comfort.
- Moisture Resistance: The height of bricks can also affect the moisture resistance of a wall. Taller bricks, when properly sealed and flashed, can help prevent moisture penetration and reduce the risk of water damage. The larger surface area of taller bricks provides a more effective barrier against water infiltration.
Understanding the connection between brick height and functional considerations is essential for architects, builders, and homeowners. By carefully considering the thermal insulation and moisture resistance requirements of a building, the appropriate brick height can be selected to optimize performance and ensure the long-term durability of the structure.
Frequently Asked Questions about Brick Height
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding brick height, providing clear and informative answers.
Question 1: What factors influence the choice of brick height?The choice of brick height is influenced by several factors, including structural requirements, aesthetic preferences, construction techniques, regional availability, and functional considerations such as thermal insulation and moisture resistance.
Question 2: How does brick height affect the strength and stability of a structure?Taller bricks generally provide better load-bearing capacity and structural stability compared to shorter bricks. This is because taller bricks distribute weight more evenly, reducing stress concentrations and increasing the overall strength of the structure.
Question 3: Can brick height enhance the aesthetic appeal of a building?Yes, brick height plays a significant role in the aesthetic appearance of a building. Different brick heights can create diverse patterns, textures, and visual effects, adding depth, character, and visual interest to facades and architectural features.
Question 4: How has brick height evolved over time?Brick height has evolved alongside advancements in construction techniques and material availability. In ancient times, bricks were often taller and narrower, while modern bricks tend to be shorter and wider. This evolution reflects changes in construction practices, firing techniques, and regional preferences.
Question 5: What are the functional implications of brick height?Brick height can impact a building's thermal insulation and moisture resistance. Taller bricks provide better thermal insulation by absorbing and storing heat, while also enhancing moisture resistance by reducing water penetration.
Question 6: How can architects and builders leverage brick height effectively?Architects and builders can harness the potential of brick height by carefully considering its impact on structural performance, aesthetic appeal, and functional requirements. Understanding the relationship between brick height and these factors enables them to make informed decisions, resulting in durable, visually pleasing, and energy-efficient structures.
These FAQs provide valuable insights into the significance and considerations surrounding brick height. By addressing common questions, this section empowers readers with a comprehensive understanding of this essential aspect of brickwork.
Transition to the next article section:
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of brick height, we have delved into its multifaceted significance in the realm of architecture. From its impact on structural integrity and aesthetic appeal to its functional implications and historical evolution, brick height stands as a cornerstone of architectural design.
Understanding the intricate relationship between brick height and these factors empowers architects, builders, and homeowners to make informed decisions that optimize the performance, durability, and visual impact of brick structures. As we continue to push the boundaries of architectural innovation, brick height will undoubtedly remain a vital consideration, inspiring creativity and shaping the built environment of the future.


Detail Author:
- Name : Dr. Gianni Gutmann
- Username : mgleason
- Email : bpfannerstill@ratke.com
- Birthdate : 1998-04-19
- Address : 785 Weissnat Estates Dessiefurt, ND 56535-0170
- Phone : +1 (302) 713-3387
- Company : Eichmann-Quigley
- Job : Model Maker
- Bio : Quo nostrum et magni quia laborum similique eius. Voluptas officia non vero velit. Et recusandae in ipsum commodi laudantium. Quia velit dolorum quo et repellendus.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/juliethammes
- username : juliethammes
- bio : Ex magnam rerum maiores rerum. Et et laboriosam est voluptas.
- followers : 6979
- following : 890
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/juliet_hammes
- username : juliet_hammes
- bio : Similique et eum et.
- followers : 290
- following : 1009
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/juliet.hammes
- username : juliet.hammes
- bio : Quia atque qui excepturi nisi qui. Qui veniam ut veniam aliquam. A qui velit molestiae ipsam.
- followers : 4750
- following : 1359